OSTEOPOROSIS
Osteoporosis is associated with the decrease of calcium content in bones. It reduces the mechanical strength of bones, and even slight load could cause the bone fracture. Osteoporosis and pathological spine fractures develop in postmenopausal women due to hormonal changes, and also in men due to incorrect diet. The pathological fracture usually occurs in hips and thoracic or lumbar vertebrae. These bones have thin cortex (it makes bone stronger) and good circulation in spongious layer ( the largest component of hip and vertebrae). It predisposes them to quick resorption and bone reduction at osteoporosis. These regions can develop the terrible complication of disease by pathological spine fracture.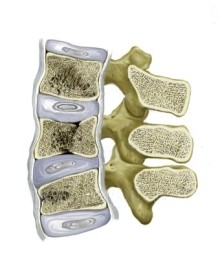
After the insignificant load, and sometimes also without it, – patients note crunch and sudden pain in the back. It occurs, when the strength of vertebra reaches its limit, and it cannot support the weight of body any longer. In this case height of vertebra decrease sharply – in pathological fracture vertebra 'collapses' leading to spine deformation, associated with persistent pain. Subsequently the vertebra sets, but pain continue for a long time, because of the failure in support function and spine deformation.
Densitometry
Densitometry helps to predict these changes, and establish diagnosis at an early stage. In densitometry, affected vertebrae are targeted with X-ray. Bone calcium retains some part of radiation. In the case of high calcium content, bone retains more radiation, and it is recorded by the sensor. These data are compared with the numbers for a healthy spine, and bone density is determined precisely. This method helps to verify the diagnosis of osteoporosis and to determine its degree.Treatment
At the early stage, before the pathological spine fractures, osteoporosis can be treated with medical therapy. It includes drugs that stop calcium washing from the bone, and induce reconstruction of bone crystal matrix to increase its strength.The first line includes Miacalcic, Calcium-D3-Nikomed. The second line includes Fosamax, Bonviva, Aklasta.
Osteoporosis requires prolonged treatment and regular monitoring of calcium level in bone tissue. Usually, patients should have densitometry once a year to control the effectiveness of therapy.
Surgical treatment
Some time ago pathological spine fractures in patients with osteoporosis were absolute contraindications for surgical treatment due to high blood loss and low bone density. During surgery bone fell to pieces, screws came out of the bone, and clinical outcome was disappointing both for patients and surgeons. But with new technologies, in particular with the invention of bone cement, surgery in osteoporosis became possible. Today this technology is proven to be safe and effective. New cement formulation is more convenient, decreases the risk of complications, and allows combination with other surgical methods.New minimally invasive methods of percutaneous vertebroplasty and stenting are widely used in the treatment of pathological spine fractures in patients with osteoporosis, especially in elderly patients (70-80 y).
Vertebral stenting is very effective in restoring the shape and support function of the broken vertebra. Unfortunately, vertebral stenting works only in 2-3 weeks after the injury. Later the effectiveness of this procedure decreases due to fracture consolidation. In such cases, isolated vertebroplasty with high viscosity bone cement is recommended. It also has excellent immediate and long-term results.
The minimally invasive percutaneous procedures require only short duration of anesthesia (up to 15-20 min), which is particularly important for elderly patients. It helps to avoid severe stress for the organism, and patients can stand up and walk immediately after the procedure. In 1-2 days after the operation, patients are discharged from the hospital and can get back home or stay in the rehabilitative center.
In unstable fractures more complicated procedure is required - spine transpedicular fixation using cannulated screws with the simultaneous vertebroplasty. This technology helps to overcome previous limitations of surgery in osteoporosis, but nevertheless, due to its complexity and duration, this operation is performed only in selected cases, mostly in young patients. After this procedure patients stand up and walk in 2-3 days, and the average period of a stay in the hospital is up to 10 days.
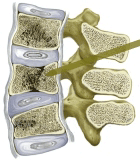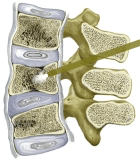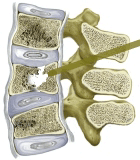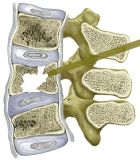 |
vertebroplasty |
 |
balloon kyphoplasty |
 |
Vertebral stenting |
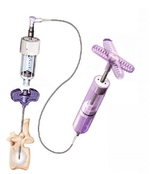 |
Confidence |
 |
transpedicular fixation using cannulated screws with the simultaneous vertebroplasty |


