Types of disc herniation
Disc herniations are distinguished by the localization, the size, the time of onset, and the level of the spine.
For example, Schmorl's nodule looks like a void space in a vertebra, with its base inverted to the side of the disc. It was described by the German doctor at the beginning of XX century. Such lesions do not affect support and dynamic functions of the spine and do not require special treatment. Spinal surgeons call them a "birth mark on the vertebra.''
Frontal herniation is benign, but rare type of herniation. Anterior disc prolapse is quite often an unexpected finding; it does not require special treatment.
Posterior herniation protrudes backward, into the spinal channel. It could require surgical treatment. It is the most common type of herniation. It requires surgery if a patient does not respond to medical therapy during 4-8 weeks.
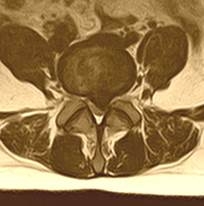
| Median herniation is uncommon and in all cases it locates at the level L5-S1. In the case of large herniation, surgery is necessary to prevent impaired function of pelvic organs. | 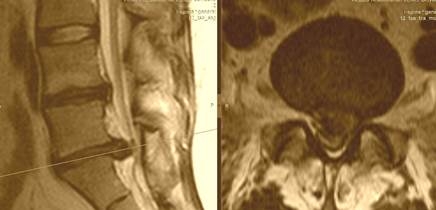 |
 |
Paramedial disc herniation is the most common type of herniation in patients referred to a surgeon. In this case, herniation locates at the cuff of the nerve root, the most painful place. It causes the compression of dural sac and several nerve roots, which slurs the classic neurological signs of disease. Such patients can have a good response to medical treatment, but eventually, they are referred to a neurosurgeon for spine surgery. After the procedure many patients are wondering why they suffered from pain such a long time – they did not know that operation is an easy and fast way to live without the pain. |
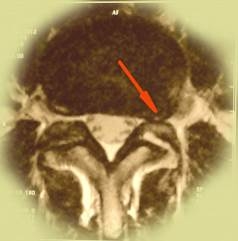
| Lateral herniation is the second most common type of disc herniation. In this case, disc breaks through the spinal ligaments to the lateral pouch – the narrowest place at the entrance of nerve root into the spinal channel. In these cases, usual painkillers are not effective, and patients suffer from persistent pain in lower limbs. Such patients, having tested many therapies, rapidly agree to the spinal surgery when they learned about the exact reason of this persistent pain. | 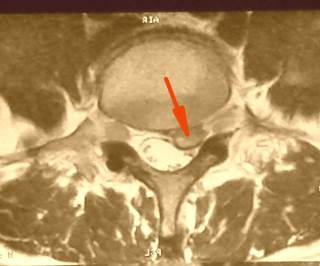 |
 |
Foramen herniation is a rare type and could be associated with isthmic spondylolysis. Spiral computed tomography helps to diagnose this condition. Foramen herniation presents some difficulties for diagnostics, as there is no herniation in the spinal channel, despite severe pain. In this case, a small (only 3-4 mm) herniation locates in the very bottleneck - vertebral foramen opening, where the little piece of cartilage compresses the nerve root. This condition requires surgery. |
Ekstraforamen herniation (or posterolateral herniation) is also quite a rare condition, difficult to diagnose. In this case big sequestration breaks through fibrous ring over the posterior-lateral surface, it falls into the region of neurovascular bundle, it separates nerves and vessels and wraps the nerve root from all sides. Pain is local, persistent and does not change with body position. Surgery removes pain quickly and efficiently.
Sequestered herniation contains a small piece of nucleus pulposus. It's an absolute indication for surgery.
Sequestered herniation with migration happens when the disc protrudes in the spinal channel upward or downward. This fragment is hard to find during the surgery. It is frequently accompanied by hemorrhage from the varicose epidural veins and is associated with the high risk of the damage to nerve root or dural sac. This condition was the reason for bad rumors about spinal surgery being connected with the high risk of complications and disability. Such delicate surgery requires sophisticated equipment, including a surgical microscope, good light, bipolar and monopolar coagulation, microsurgical instruments, and the primary factor – an experienced surgeon, who will gently isolate and free nerve root, removing disc herniation.
| Calcified herniation is always an unexpected finding, especially if CT was not performed before surgery. Unfortunately, MRI does not show disc calcification. Calcified herniation is difficult to remove, and surgeon requires an additional set of instruments. Therefore in our clinic, we always do both CT and MRI before the spinal surgery. | 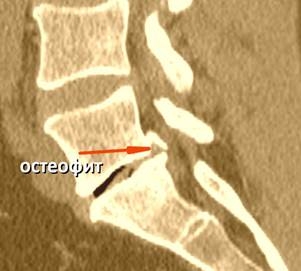 |


