Spine examination before surgery
Back pain in any given situation — bad weather or incorrect loading on the spine, or diet violation and excessive weight — may happen in the life of each person. As a rule, realizing the cause of back pain in time, and removing it (warming up in the case of bad weather, spreading the load correctly when lifting weights, and healthy eating to eliminate excess weight) helps to avoid more serious problems with the spine.But what to do, if the pain does not pass, though you are doing everything right — no cold, no heavy lifting, getting rid of extra weight, but the pain is persistent and even irradiates into the foot?
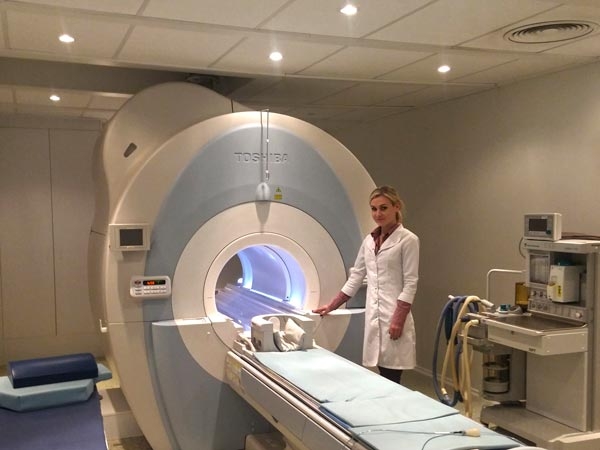
MRI helps to understand the cause of chronic back pain. Modern MRI has the strength of the magnetic field 1,5 Tesla — more than enough to diagnose spine problems. During MRI patient stays for a short time in a powerful magnetic field, which being turned off causes emission from hydrogen atoms in the human body. Special sensors in MRI scanner catch those electromagnetic waves. Sensor data is analyzed using a complex algorithm, and then a virtual slice of the body area is produced. Body structures reach in hydrogen, primarily water and fat, are clearly seen in MRI scan. To distinguish fat from water, your doctor uses a special filter for fat suppression - STIR. Body structures with low water contents, such as bony structures, are not clearly visible on MRI.
Old scanners with 0.15, 0.2, 0.3 or 0.5 Tesla give scans of low quality, on which it is impossible to distinguish between minor details because they have quite low-resolution capability to 5 or even 10 mm. MRI is crucial to assess the severity of degenerative-dystrophic changes and diagnose disc protrusion or herniation. MRI also shows tumors, stenosis of the spinal canal, and helps to suspect the presence of osteophytes. Most importantly, why MRI is assigned in the first place — it's very effective: MRI immediately shows if there is a compression of neural structures.
However, MRI requires heavy equipment. MRI machine weighs several tons and requires a reliable foundation. Also during MRI patient stays for some time inside the small closed chamber, and it becomes a real problem for claustrophobic patients. In such patients and in tall or overweight patients, which do not fit standard MRI machine, the examination can be performed with open circuit scanner. Such MRI will have lower resolution, but it bears no restriction on patient weight and height.
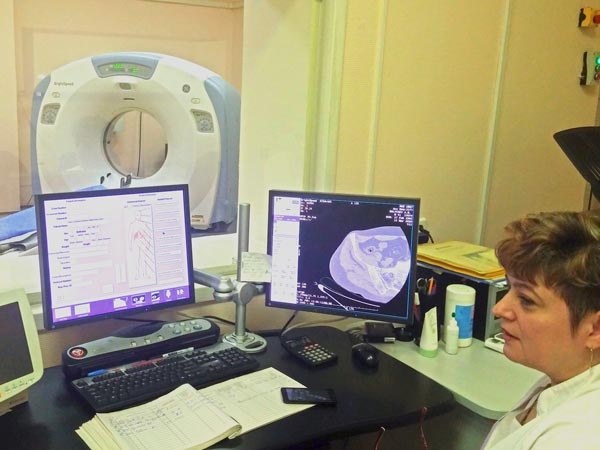
CT also plays an important role in spine examination. A CT scan makes use of computer-processed combinations of many X-ray images taken from different angles to produce cross-sectional (tomographic) images (virtual "slices") of specific areas of a scanned object, allowing the user to see inside the object without cutting. Digital geometry processing is used to generate a three-dimensional image of the inside of the object from a large series of two-dimensional radiographic images taken around a single axis of rotation. To accelerate an examination, contemporary tomographs contain many pairs emitter-receiver — 2, 4, 8, 16, the most modern — up to 64! In this case, examination lasts second, and the rest of the time is spent on scanner adjustment for the particular patient. Modern CT scanners give the precise and clear spine image, which helps to establish a correct diagnosis and plan spine surgery in advance.
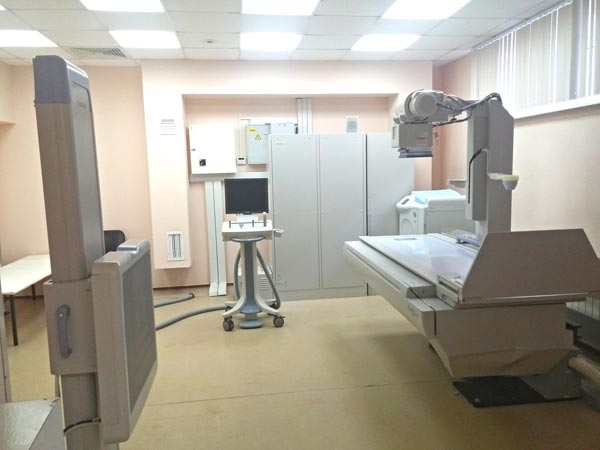
Spine X-ray
- Checked by time, reliable, accessible, simple and informative method offering a nice field of view. With spine X-ray scans experienced doctor can establish a diagnosis in the majority of patients with the traumatic damages of the spine. All the remaining methods are conducted for refining of diagnosis and procedure planning to decrease its invasiveness. For procedure planning and postoperative follow up your doctor will do a standard X-ray in two planes and functional scans in flexion and extension. Spine X-ray identifies spinal fractures and dislocations, spondylolysis, spondylolisthesis, segmental instability. Contemporary digital scanners provide excellent digital quality and reduce the radiation exposure (in comparison with the old models) due to the highly sensitive matrix.
Scintigraphy is a diagnostic test in nuclear medicine, where radioisotopes attached to drugs that travel to a specific organ or tissue (radiopharmaceuticals) are taken internally, and the emitted radiation is captured by external detectors (gamma cameras) to form two-dimensional images in a similar process to the capture of x-ray images. The subjects are injected with special radionuclides which irradiate in the gamma range inside the region of interest. Depending on the intensity of accumulation and uniformity of the distribution of radiopharmaceutical preparation, it is possible to judge nature of the disease and its extent. This method has high diagnostic value for cancer screening.
.
- Checked by time, reliable, accessible, simple and informative method offering a nice field of view. With spine X-ray scans experienced doctor can establish a diagnosis in the majority of patients with the traumatic damages of the spine. All the remaining methods are conducted for refining of diagnosis and procedure planning to decrease its invasiveness. For procedure planning and postoperative follow up your doctor will do a standard X-ray in two planes and functional scans in flexion and extension. Spine X-ray identifies spinal fractures and dislocations, spondylolysis, spondylolisthesis, segmental instability. Contemporary digital scanners provide excellent digital quality and reduce the radiation exposure (in comparison with the old models) due to the highly sensitive matrix.
Scintigraphy is a diagnostic test in nuclear medicine, where radioisotopes attached to drugs that travel to a specific organ or tissue (radiopharmaceuticals) are taken internally, and the emitted radiation is captured by external detectors (gamma cameras) to form two-dimensional images in a similar process to the capture of x-ray images. The subjects are injected with special radionuclides which irradiate in the gamma range inside the region of interest. Depending on the intensity of accumulation and uniformity of the distribution of radiopharmaceutical preparation, it is possible to judge nature of the disease and its extent. This method has high diagnostic value for cancer screening.

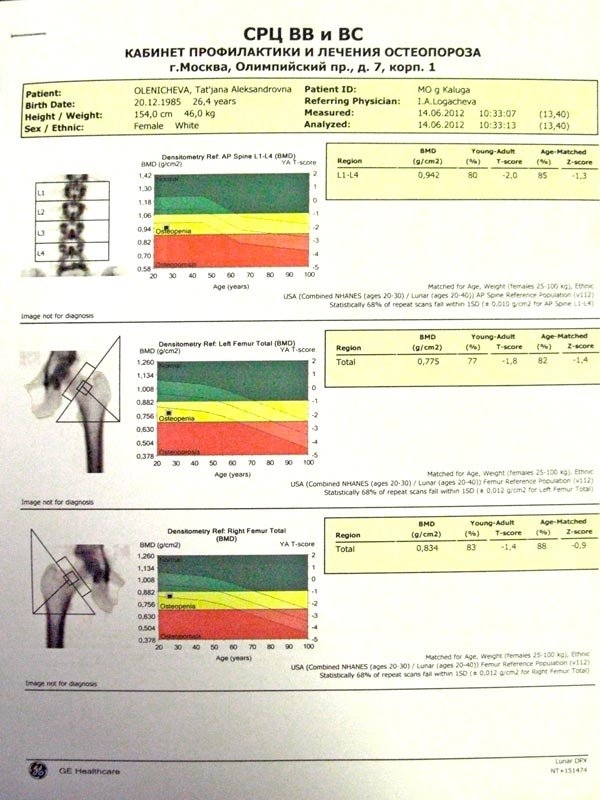
Spine densitometry is the method, mostly used for the diagnostics of osteoporosis. Computer algorithm calculates the X-ray attenuation for each lumbar vertebra (L1, L2, L3, L4 vertebrae), compares it with the standard indices for each vertebra, with the correction to the age. Results of densitometry can show normal condition (T-index positive or 0 to -1.0), osteopenia (T-index -1.0 to -2.5) and osteoporosis (T-index is less -2.5). In the case of the pathological fractures, the vertebrae become denser, and mineral density of the fractured vertebra increases, which gives a false thought about osteoporosis. Therefore osteoporosis can be established only by clinician taking into account all data.
For a long time, osteoporosis was an absolute contraindication to spinal reconstruction and fixation. In such patients only vertebroplasty with bone cement was possible. Only in the middle of 2000s appeared new devices, which were approved for complex reconstructive spinal surgery in patients with osteoporosis.
Spine ultrasound examination is not widely used in practice because of the small depth of scanning and a large number of artifacts. CT and MRI provide all necessary information about the spine.
Ultrasound is common for diagnostics of vascular diseases, such as obstruction of arterial and venous blood flow, as well as thrombus, including differential diagnosis between sural thrombosis and L5 radiculopathy, and for prevention of severe thromboembolic complications.
For a long time, osteoporosis was an absolute contraindication to spinal reconstruction and fixation. In such patients only vertebroplasty with bone cement was possible. Only in the middle of 2000s appeared new devices, which were approved for complex reconstructive spinal surgery in patients with osteoporosis.
Spine ultrasound examination is not widely used in practice because of the small depth of scanning and a large number of artifacts. CT and MRI provide all necessary information about the spine.
Ultrasound is common for diagnostics of vascular diseases, such as obstruction of arterial and venous blood flow, as well as thrombus, including differential diagnosis between sural thrombosis and L5 radiculopathy, and for prevention of severe thromboembolic complications.
.


